Introduction
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, efficient content management is the key to success. Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) Workflow is a robust tool that can help organizations streamline their content management processes, ensuring that content creation, approval, and publishing are seamless and efficient. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into AEM Workflow, exploring its features, benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding AEM Workflow
What is AEM Workflow?
Adobe Experience Manager Workflow, often referred to as AEM Workflow, is a powerful content management system designed to automate and optimize various content-related tasks within an organization. It allows for the efficient creation, review, approval, and publication of content, ensuring a smooth and controlled content management process.
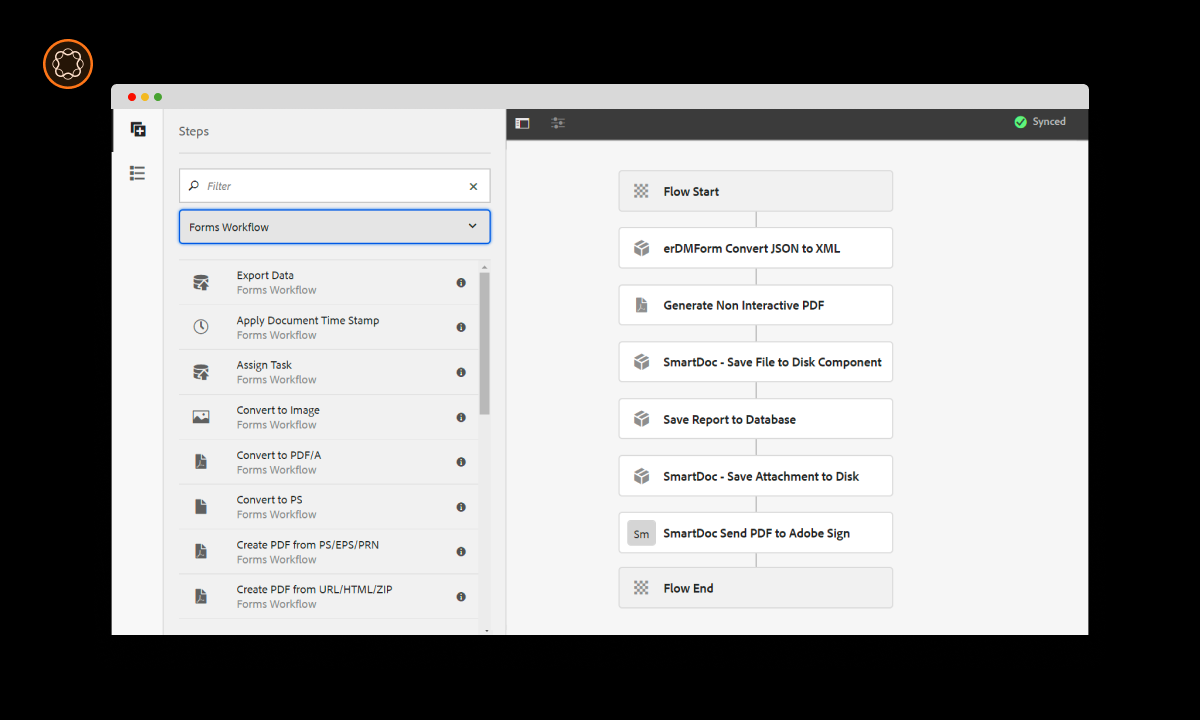
Key Components of AEM Workflow
Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) Workflow is a comprehensive content management system designed to streamline and optimize content-related processes. To grasp its functionality better, let’s break down its key components:
Workflow Models
Workflow models in AEM Workflow serve as the backbone of the system. These are predefined templates that meticulously outline the structure and flow of content-related processes within an organization. Each workflow model is designed to address specific content management needs, making it adaptable to various scenarios.
AEM Workflow Models Include:
- Sequential Workflows: These models follow a linear progression, where tasks are completed in a predetermined order. Ideal for straightforward content creation and approval processes.
- Parallel Workflows: In parallel workflows, multiple tasks can be executed simultaneously. This is beneficial for scenarios where different aspects of content need to be worked on concurrently.
- Conditional Workflows: These models allow for branching based on specific conditions. For instance, if a content piece requires different approval processes based on its type, a conditional workflow can accommodate this complexity.
Workflow Steps
Workflow steps represent the individual actions or tasks that need to be completed as part of a content workflow. These steps can be highly customized to match an organization’s specific content management requirements. Each step is assigned a purpose and may involve various stakeholders, including content creators, editors, and approvers.
Common Workflow Steps in AEM Workflow Include:
- Content Creation: Initiating the workflow with the creation of a new piece of content, ensuring it adheres to predefined templates and guidelines.
- Content Review: Content undergoes a comprehensive review process, with designated reviewers providing feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Content Approval: Once reviewed, content moves to the approval stage, where authorized individuals or teams grant final approval for publication.
- Publishing: After approval, content is published to the designated channels, making it accessible to the intended audience.
Participants
Participants are the individuals or groups involved in carrying out specific workflow steps. AEM Workflow assigns tasks to participants based on predefined rules, roles, and permissions. This ensures that the right people are responsible for the right tasks at the right time.
Key Aspects of Participants in AEM Workflow:
- Roles and Responsibilities: Participants are assigned roles within the workflow, such as content creator, editor, or approver. Each role comes with specific responsibilities and permissions.
- Notifications: Participants receive automated notifications about pending tasks, deadlines, and updates within the workflow. This keeps everyone informed and ensures timely action.
- Escalation: In case a task is not completed within the specified timeframe, AEM Workflow can escalate it to higher authorities or backup participants to avoid workflow bottlenecks.
Notifications
Effective communication is essential in any content management workflow. AEM Workflow includes a robust notification system to keep participants informed throughout the process. Notifications can be customized to suit the organization’s preferences and needs.
Types of Notifications in AEM Workflow:
- Task Assignment: Participants receive notifications when a task is assigned to them, along with details about the task and its deadline.
- Status Updates: Participants are informed when the status of a task changes, such as when content moves from the review to approval stage.
- Deadline Reminders: Automated reminders ensure that participants are aware of upcoming task deadlines, helping to maintain workflow efficiency.
By understanding these key components of AEM Workflow in more detail, organizations can harness its power to create efficient, customized content management processes that align with their specific needs and goals.
Benefits of AEM Workflow
Enhancing Efficiency
AEM Workflow significantly enhances content management efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, reducing manual intervention, and minimizing errors.
Improved Collaboration
With AEM Workflow, teams can collaborate seamlessly, ensuring that content creators, editors, and approvers work together harmoniously.
Version Control
AEM Workflow maintains version control, allowing users to track changes and revert to previous versions if needed.
Compliance and Security
AEM Workflow offers robust security features, ensuring that content remains compliant with regulatory requirements and confidential information is protected.
Implementing AEM Workflow in Your Organization
Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) Workflow can be a transformative addition to your organization’s content management strategy. To ensure a successful implementation, consider the following detailed steps:
Creating Workflow Models
Identify Content Processes
Begin by identifying the specific content management processes within your organization that can benefit from automation and streamlining. Common processes include content creation, review, approval, and publishing.
Design Custom Workflow Models
- Gather Requirements: Collaborate with key stakeholders, including content creators, editors, and approvers, to understand their needs and expectations from AEM Workflow.
- Model Creation: Using the AEM Workflow interface, create custom workflow models that align with your organization’s unique content processes. Consider using different workflow types (sequential, parallel, conditional) for various scenarios.
- Sequence Tasks: Define the sequence of tasks within each workflow model, including the participants involved in each step and the dependencies between tasks.
- Testing and Validation: Test your workflow models with a small group of users to identify any potential issues or areas for improvement. Make necessary adjustments based on feedback.
Using AEM Workflow
Content Creation
- Initiating Workflows: When content creation is initiated, select the appropriate workflow model based on the type of content being created. Ensure that all required fields and information are filled out as per the workflow’s specifications.
- Automatic Task Assignment: AEM Workflow will automatically assign tasks to the relevant participants based on the predefined rules and roles within the workflow model.
Review and Approval
- Reviewer Collaboration: Content goes through a review process where designated reviewers provide feedback and suggestions for improvement. AEM Workflow facilitates collaboration among reviewers.
- Approval Workflow: Once content is reviewed and updated, it moves to the approval stage, where authorized individuals or teams grant final approval for publication.
c. Publishing
- Publication Automation: After approval, AEM Workflow automates the publishing process, ensuring that content is disseminated to the designated channels, such as websites, mobile apps, or social media platforms.
- Version Control: AEM Workflow maintains version control, allowing users to track changes and revert to previous versions if needed.
Best Practices for AEM Workflow
Regularly Update Workflow Models
As your organization evolves, update your workflow models to align with changing content management requirements.
Train Your Team
Ensure that your team is well-trained in using AEM Workflow to maximize its benefits.
Monitor and Analyze
Regularly monitor workflow performance and analyze data to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
AEM Workflow Purging
Identify workflows with significant data and set retention periods based on business needs. Use AEM’s built-in purging features and schedule tasks during off-peak hours. Purge completed or aborted workflows after a set period, avoiding in-progress ones. Regularly monitor and adjust purging tasks. Backup critical data before purging and consider archiving essential information. Automate and optimize purging scripts to prevent system overload. Test purging in a staging environment first, then document the setup and train team members. Ensure compliance with regulations and periodically review policies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Adobe Experience Manager Workflow is a powerful tool for streamlining content management processes within organizations. By automating tasks, enhancing collaboration, and ensuring compliance, AEM Workflow empowers businesses to manage their content efficiently and effectively.

I’m Kirill Efimov, an experienced AEM developer with over 10 years of experience in Java and web development. I’m skilled in developing AEM components, templates, workflows, and integrations with other systems, and I’m passionate about delivering high-quality solutions to my clients.
I also believe in knowledge-sharing and staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the industry. Through blog posts, tutorials, and speaking engagements, I’m committed to contributing to the AEM community and helping others overcome the challenges they may face in their AEM projects.