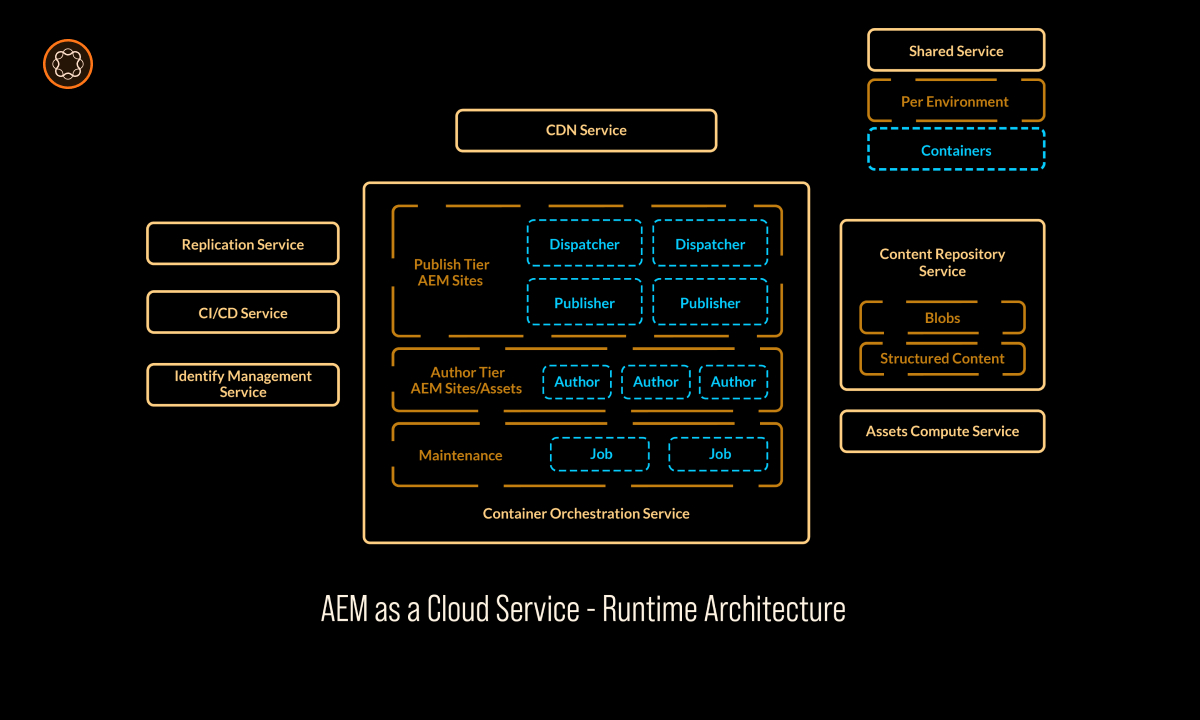
Introduction to AEM Cloud Architecture
Adobe Experience Manager, commonly known as AEM, is a powerful content management solution designed to streamline the creation, management, and delivery of digital content. In an era where online engagement is pivotal, AEM plays a crucial role in enabling organizations to deliver seamless and personalized digital experiences.
Key Components of AEM Cloud Architecture
Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) Cloud Architecture comprises several essential components that work harmoniously to deliver a robust and scalable content management solution. Understanding these components is pivotal to harnessing the full potential of AEM in the cloud.
AEM (Adobe Experience Manager)
At the heart of AEM Cloud Architecture lies Adobe Experience Manager itself. AEM is a comprehensive content management system that offers a wide array of features and functionalities.
Content Repository: AEM’s content repository is where all digital assets, content, and configurations are stored. It provides a structured and secure environment for managing content, including web pages, images, videos, and documents. The repository supports versioning, allowing teams to track changes and revert to previous versions when needed.
Delivery Service: AEM’s delivery service is responsible for efficiently serving content to end-users. It optimizes content delivery for different devices and channels, ensuring that web pages load quickly and perform smoothly. This component plays a vital role in delivering seamless digital experiences.
Authoring Environment: AEM offers a user-friendly authoring environment that allows content creators and editors to easily create, edit, and organize content. It provides a WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editor and collaboration tools, simplifying content management tasks.
Integration Framework: AEM’s integration capabilities enable seamless connectivity with other systems and technologies. It supports various integration protocols, making it possible to integrate with e-commerce platforms, CRM systems, analytics tools, and more. This component ensures that AEM fits seamlessly into an organization’s technology ecosystem.
Cloud Deployment Options
AEM Cloud Architecture offers flexibility in choosing the cloud deployment environment that best aligns with an organization’s needs and strategies. The three primary cloud deployment options are:
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS provides a highly scalable and reliable cloud infrastructure. AEM can be deployed on AWS, taking advantage of services like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Amazon RDS, and Amazon S3 for robust and scalable hosting.
Microsoft Azure: Azure offers a comprehensive set of cloud services, including Azure App Service and Azure Blob Storage, which can be utilized for hosting AEM. Azure’s integration capabilities also make it a suitable choice for organizations using Microsoft technologies.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP provides a range of cloud services and tools that can support AEM deployments. Google Cloud’s global network infrastructure and data analytics capabilities can enhance the performance and scalability of AEM.
Each cloud provider brings its unique strengths to the table, and the choice depends on factors such as existing infrastructure, budget, and specific requirements.
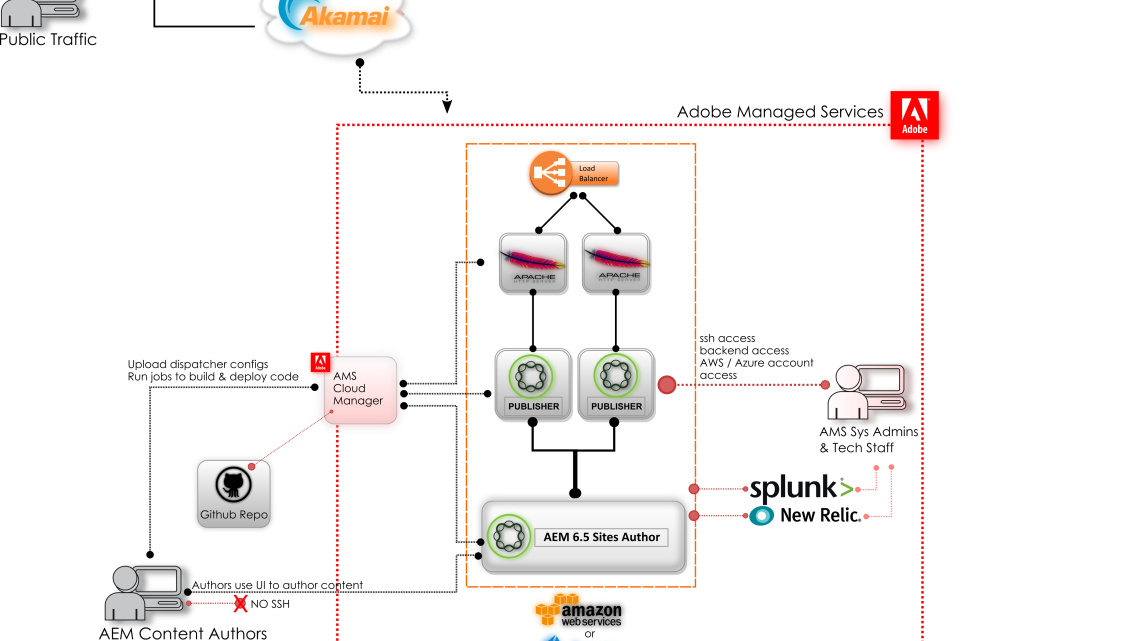
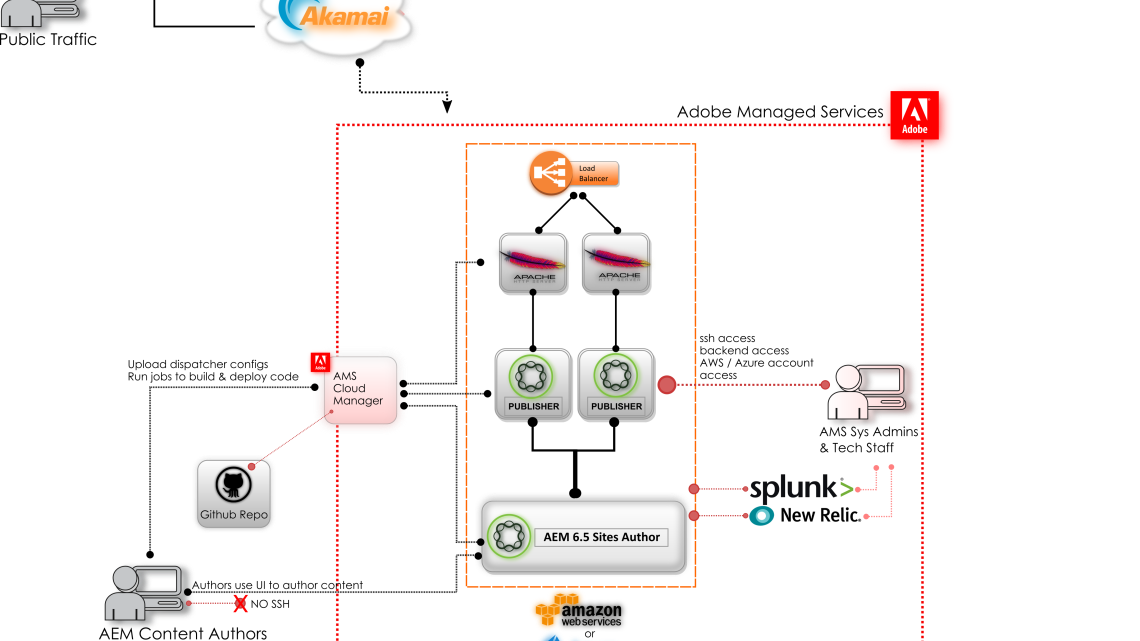
Architecture Components
AEM Cloud Architecture encompasses several key architectural components that are crucial for achieving scalability, reliability, and performance:
Dispatcher: The Dispatcher is a caching and load-balancing tool that sits in front of the AEM instance. It caches and serves static content, reducing the load on the AEM server and improving response times. It plays a vital role in optimizing the delivery of web pages.
Database: AEM relies on a database to store configuration data, user profiles, and other essential information. Various database options can be used, including relational databases like PostgreSQL and NoSQL databases like MongoDB, depending on the specific requirements of the deployment.
Scalability: Scalability is a fundamental aspect of AEM Cloud Architecture. It involves configuring the system to handle increased workloads by adding or removing resources dynamically. Horizontal scaling, in which additional instances of AEM are added, is a common approach to achieve scalability.
Load Balancer: Load balancers distribute incoming web traffic across multiple AEM instances, ensuring even distribution of workloads and high availability. This component is essential for maintaining system performance and reliability.
Understanding these key components and their interactions is essential for successfully implementing and managing AEM Cloud Architecture. Organizations can tailor their AEM deployment to meet their specific content management needs while leveraging the advantages of the cloud environment they choose.
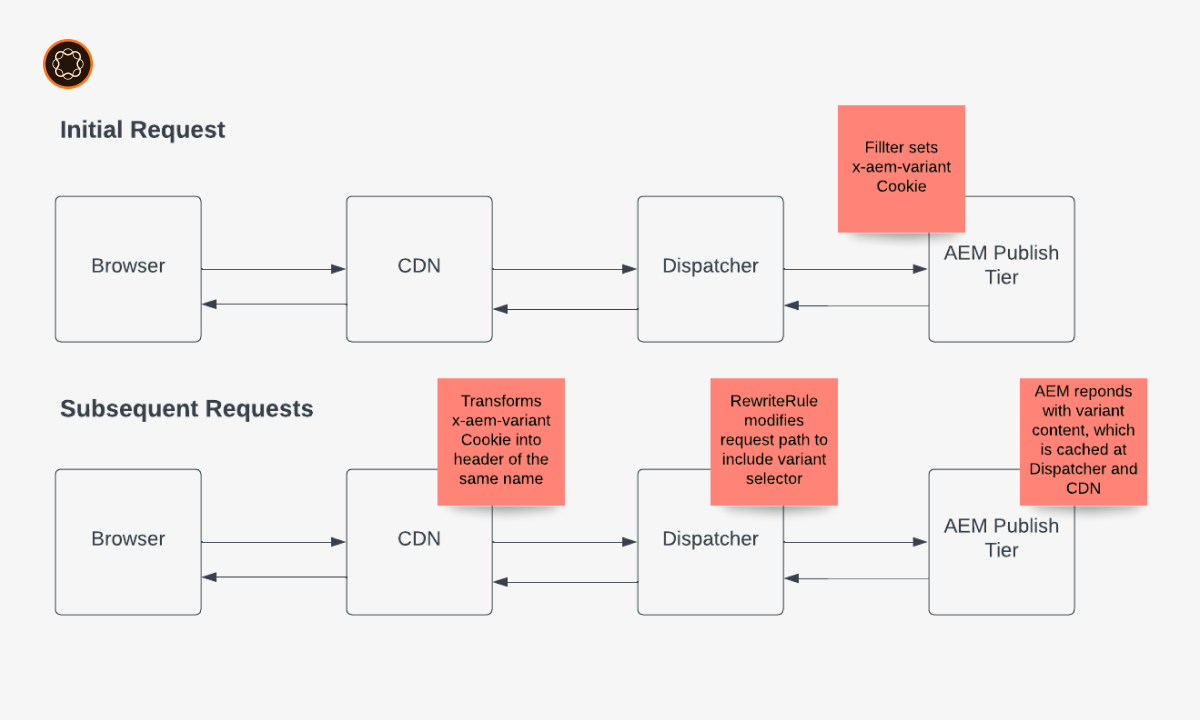
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits of AEM Cloud Architecture
Scalability
One of the standout advantages of AEM Cloud Architecture is scalability. Cloud-based deployment allows organizations to scale their resources dynamically, ensuring that they can handle increased workloads during peak times. This scalability leads to improved performance and responsiveness.
Performance
AEM’s integration with cloud services optimizes content delivery, resulting in faster loading times and improved user experiences. This performance boost is vital for retaining and engaging visitors to your digital platforms.
Cost-Efficiency
Cloud-based solutions often offer cost-efficiency through pay-as-you-go pricing models. Organizations can allocate resources based on their actual usage, reducing unnecessary expenses.
Challenges
While the cloud brings numerous benefits, it also introduces security concerns. Organizations must implement robust encryption and access control measures to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Integration
Integrating AEM with existing systems and tools can be complex. Achieving seamless connections between AEM and other components of your technology stack requires careful planning and execution.
Best Practices
In the realm of AEM Cloud Architecture, several best practices are recommended to maximize its potential.
Microservices
Adopting a microservices architecture allows organizations to break down complex applications into smaller, modular components. This approach enhances scalability, flexibility, and maintainability.
DevOps Integration
Integrating DevOps practices into the AEM deployment process leads to faster and more efficient deployments. Automation, collaboration, and continuous integration are key components of this approach.
Use Cases
To understand the real-world applicability of AEM Cloud Architecture, let’s explore two common use cases:
E-commerce Websites
AEM Cloud Architecture is well-suited for e-commerce websites. It enables businesses to manage product catalogs, handle high website traffic, and provide personalized shopping experiences.
Marketing Campaigns
For marketing professionals, AEM Cloud Architecture facilitates the rapid deployment of marketing campaigns. It allows for the creation, management, and distribution of campaign content across various digital channels.
Tools and Technologies
A successful implementation of AEM Cloud Architecture requires familiarity with specific tools and technologies.
- Adobe Experience Manager: The cornerstone of the architecture.
- Cloud Providers: AWS, Azure, GCP – Choose the one that aligns with your organization’s cloud strategy.
- Containerization: Technologies like Docker and Kubernetes can enhance deployment flexibility and resource management.
Conclusion
AEM Cloud Architecture revolutionizes how organizations manage and deliver digital content. With its scalable and performance-enhancing features, it empowers businesses to provide exceptional online experiences. While it presents challenges, the adoption of best practices like microservices and DevOps integration can help organizations overcome these hurdles and unlock the full potential of AEM Cloud Architecture. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, leveraging AEM in the cloud will remain a strategic advantage for those striving to excel in the online realm.

I’m Kirill Efimov, an experienced AEM developer with over 10 years of experience in Java and web development. I’m skilled in developing AEM components, templates, workflows, and integrations with other systems, and I’m passionate about delivering high-quality solutions to my clients.
I also believe in knowledge-sharing and staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the industry. Through blog posts, tutorials, and speaking engagements, I’m committed to contributing to the AEM community and helping others overcome the challenges they may face in their AEM projects.