Introduction
In the digital age, effectively managing and delivering content across various channels is crucial for organizations. Content Fragments and Experience Fragments are two approaches that enable the modular and reusable creation and management of content. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, use cases, benefits, and challenges of both Content Fragments and Experience Fragments, and compare their key attributes.
Content Fragments
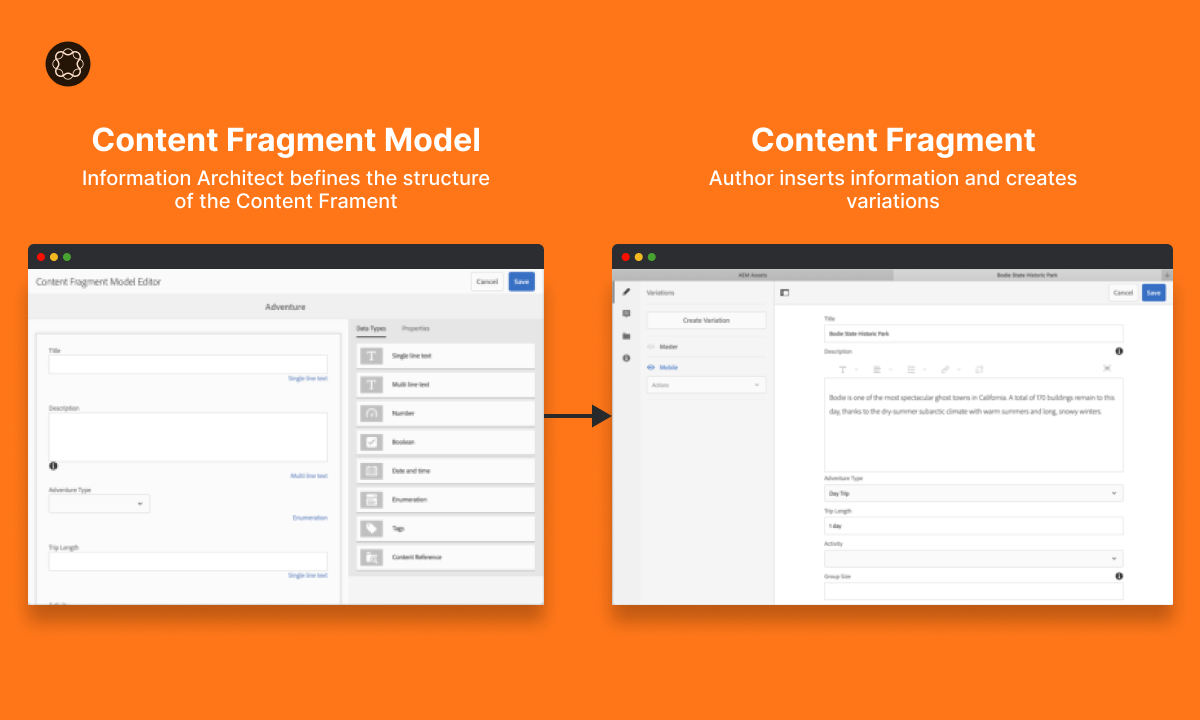
Content Fragments are versatile and modular content units that offer flexibility in creating and managing content across different channels. They provide a granular approach to content creation, enabling authors to break down information into independent and self-contained content blocks. Here’s a closer look at the key attributes and functionalities of Content Fragments:
Structure and Characteristics
Content Fragments are designed to be independent and self-contained. They can encompass various types of content, including text, images, videos, or any other form of digital media. Each Content Fragment focuses on a specific piece of content, such as a paragraph, image, or video, and is not bound to any particular design or layout. This flexibility allows for the seamless assembly of Content Fragments into larger content pieces.
Content Creation and Management
Content Fragments are created and managed within a content management system (CMS). Authors can easily create, edit, and organize Content Fragments using the CMS interface. By leveraging the intuitive controls provided by the CMS, authors can assemble and update Content Fragments, making it simple to maintain and modify content as needed. Changes made to a Content Fragment are automatically reflected wherever it is used, ensuring consistency throughout the content ecosystem.
Reusability and Benefits
One of the key advantages of Content Fragments is their high reusability. Authors can reuse Content Fragments across multiple pages, websites, or applications, eliminating the need to recreate the same content from scratch. This reusability reduces content duplication and ensures consistency in messaging and branding. Updates made to a Content Fragment are propagated to all instances where it is used, making it easy to keep content up to date and synchronized.
Personalization Capabilities
Content Fragments offer personalization capabilities, allowing authors to deliver targeted and customized content to users. By leveraging user attributes or contextual information, authors can personalize the content within a Content Fragment based on specific user segments or user preferences. This personalization enhances user engagement by delivering relevant and tailored experiences to individual users.
Content Fragments serve as powerful tools for content creation and management, enabling organizations to efficiently deliver modular and reusable content across channels. Their independent and self-contained nature, combined with the ability to personalize content, makes them valuable assets in providing engaging and customized digital experiences. By utilizing Content Fragments, organizations can streamline content creation, reduce duplication, and ensure consistency while delivering content that resonates with their audience.
Experience Fragments
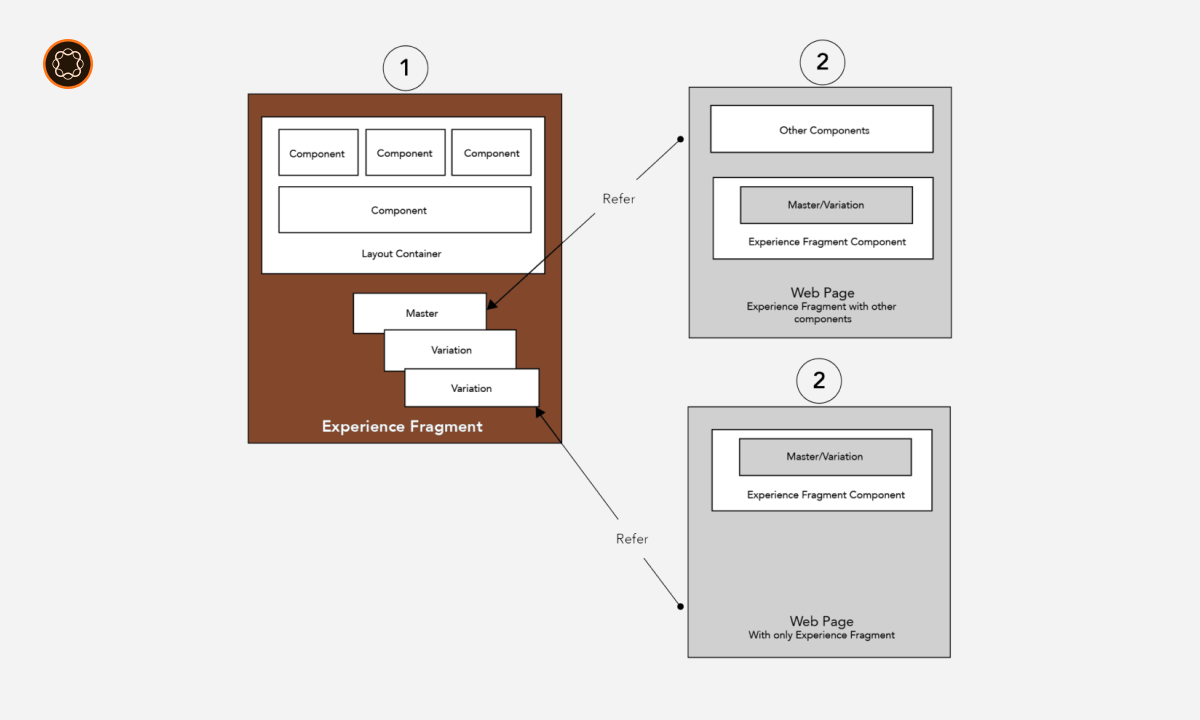
Experience Fragments are powerful tools that enable organizations to deliver consistent and reusable experiences across various channels. These predefined components combine content, design, and layout elements to create cohesive and branded experiences. Here’s a closer look at the key attributes and functionalities of Experience Fragments:
Structure and Characteristics
Experience Fragments encompass a broader scope, providing a comprehensive solution for delivering consistent experiences. They consist of multiple content fragments, media assets, and styling components, all arranged to define the structure and appearance of a specific experience or section of a website or application. By combining these elements, Experience Fragments ensure a cohesive and unified visual identity.
Content Creation and Management
Experience Fragments are created and managed within a content management system (CMS). Authors have the ability to define reusable experience components with predefined content and layout. Through the CMS interface, authors can easily assemble Experience Fragments by selecting the desired content fragments, arranging them, and applying the appropriate styling. Changes made to an Experience Fragment are automatically reflected in all instances where it is used, ensuring consistency across channels.
Reusability and Benefits
One of the key advantages of Experience Fragments is their reusability. They can be employed across different pages, websites, or applications to maintain consistent branding and messaging. By utilizing predefined experience components, organizations save time and effort that would otherwise be spent on developing custom experiences for each channel. Experience Fragments streamline the content delivery process and facilitate a unified brand experience for users.
Personalization Capabilities
Experience Fragments offer personalization capabilities, allowing organizations to tailor experiences based on user attributes or contextual information. By leveraging user data, authors can dynamically modify the content, design, and layout within an Experience Fragment to deliver targeted experiences. This personalization enhances user engagement and satisfaction by providing relevant and customized content.
Experience Fragments serve as valuable assets for organizations striving to create consistent and branded experiences across channels. They streamline the content management process, facilitate reusability, and provide the means to personalize user experiences. By leveraging the power of Experience Fragments, organizations can deliver cohesive, engaging, and tailored digital experiences that leave a lasting impression on their audience.
Comparison of Content Fragments and Experience Fragments
To better understand the differences and similarities between Content Fragments and Experience Fragments, let’s delve deeper into their key attributes and functionalities:
Purpose
- Content Fragments: Content Fragments primarily serve as modular content units that offer flexibility in their usage across different channels. They focus on creating and managing independent and reusable content blocks that can be combined to form larger content pieces.
- Experience Fragments: Experience Fragments, on the other hand, are designed to provide predefined experience components that deliver consistent and reusable experiences across channels. They aim to create cohesive and branded experiences by combining content, design, and layout elements.
Structure
- Content Fragments: Content Fragments are independent and self-contained content blocks. They typically contain a specific piece of content, such as a paragraph, image, or video. Content Fragments can be granular and are not bound to any particular design or layout.
- Experience Fragments: Experience Fragments encompass a broader scope, combining content, design, and layout elements. They are composed of multiple content fragments, media assets, and styling components. Experience Fragments define the structure and appearance of a specific experience or section of a website or application.
Content Creation and Management
- Content Fragments and Experience Fragments are both created and managed within a content management system (CMS). Authors can leverage the CMS interface to create, edit, and organize fragments.
- Content Fragments: Authors can easily assemble content fragments to create larger content pieces. Changes made to a content fragment are automatically reflected wherever it is used, ensuring consistency and reducing redundancy.
- Experience Fragments: Authors can create reusable experience components by defining the content, design, and layout elements within an experience fragment. Modifications made to an experience fragment propagate across all instances, guaranteeing consistent experiences.
Reusability
- Content Fragments and Experience Fragments share a common advantage in terms of reusability.
- Content Fragments: These modular units can be reused across multiple pages, websites, or applications. They offer granular and versatile content components that can be utilized in various contexts.
- Experience Fragments: Similar to Content Fragments, Experience Fragments can also be reused across different channels. They allow for the consistent delivery of predefined experience components, ensuring uniform branding and messaging.
Personalization
- Both Content Fragments and Experience Fragments offer personalization capabilities, enabling tailored experiences for users.
- Content Fragments: These modular units can be personalized based on user attributes or contextual information. Authors can dynamically deliver different content variants to specific user segments, enhancing engagement and relevance.
- Experience Fragments: Experience Fragments, too, can be personalized based on user attributes or contextual information. By leveraging user data, authors can deliver targeted experiences, customizing the content, design, and layout within an experience fragment.
By considering these attributes, organizations can make informed decisions about whether to utilize Content Fragments, Experience Fragments, or a combination of both, based on their specific content management and delivery needs. The choice between these approaches depends on factors such as the level of modularity required, the need for consistent experiences, the complexity of content and design, and the desired level of personalization.
Understanding the distinctions and overlapping functionalities of Content Fragments and Experience Fragments empowers organizations to architect robust and flexible content management strategies that deliver engaging, reusable, and personalized digital experiences.
Use Cases
Content Fragments and Experience Fragments find applications in various scenarios. Let’s explore some use cases for each:
Content Fragments
- Use case 1: Creating product descriptions that can be reused across different product pages.
- Use case 2: Managing legal disclaimers that need to be consistent throughout a website.
- Use case 3: Creating modular blog post components such as headings, paragraphs, and images.
Experience Fragments
- Use case 1: Building reusable hero sections with consistent branding and messaging across pages.
- Use case 2: Creating predefined product showcases that can be used on different landing pages.
- Use case 3: Developing consistent call-to-action sections for promotional campaigns.
Benefits of Content Fragments
Content Fragments offer several benefits that enhance content management and delivery:
- Modularity enables flexibility in assembling content across channels.
- Reusability reduces content duplication and ensures consistent messaging.
- Personalization capabilities enhance user engagement and satisfaction.
- Efficient content updates propagate changes across multiple instances.
Benefits of Experience Fragments
Experience Fragments provide distinct advantages for delivering consistent experiences:
- Predefined components ensure brand consistency across different channels.
- Reusability saves development time and effort.
- Personalization capabilities allow for targeted user experiences.
- Easy content updates reflect changes in all instances of an experience fragment.
Challenges and Considerations
While Content Fragments and Experience Fragments offer numerous benefits, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Choosing the appropriate approach based on the specific requirements of a project.
- Establishing an efficient workflow for creating and managing fragments.
- Ensuring proper governance and maintenance of fragment libraries.
- Integrating with other systems or platforms to leverage the full potential of fragments.
Conclusion
In the realm of content management and delivery, both Content Fragments and Experience Fragments provide valuable solutions. Content Fragments excel in their modular nature, allowing for flexible reuse and personalized content delivery. On the other hand, Experience Fragments offer predefined components that ensure consistent branding and user experiences across channels. By understanding their unique characteristics, organizations can leverage the power of both approaches to create engaging, personalized, and consistent digital experiences.

I’m Kirill Efimov, an experienced AEM developer with over 10 years of experience in Java and web development. I’m skilled in developing AEM components, templates, workflows, and integrations with other systems, and I’m passionate about delivering high-quality solutions to my clients.
I also believe in knowledge-sharing and staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the industry. Through blog posts, tutorials, and speaking engagements, I’m committed to contributing to the AEM community and helping others overcome the challenges they may face in their AEM projects.